n the digitization era, the adoption of innovative strategies for IT infrastructure management has become imperative to ensure agility, security and efficiency. GitOps methodology emerges as a cutting-edge solution to address these needs, , promising infrastructural modernization that marks a turning point in the IT landscape. In this article we will attempt to perform an in-depth analysis, aided by a meaningful case study, of how the GitOps approach can be successfully implemented to transform a legacy IT infrastructure into a modern, flexible and optimized system.
Our case study starts precisely from an infrastructure modernization process to initiate application delivery practices (CI/CD). The methodologies introduced enable several benefits, including cost reduction, enhanced security, reduced release time, and process automation. Results that could not be acquired otherwise.
The challenge and the solution
The customer wanted to understand whether their application development and management model, which is strongly tied to a legacy environment and approach, could be applied to the container world without being completely disrupted.
In a context of uncertain outcome, in the first phase of the project, the customer preferred to use a fully open-source container orchestration solution.
This choice allowed Sorint to evaluate the proposal while limiting the costs associated with purchasing product subscriptions.
For infrastructure management, the proposed solution is an ecosystem composed of the following technology components:
- Gitlab CE(Community Edition): Versioning and (CI/CD) Pipeline
- HashiCorp Vault (Community Edition): Secret management
- Kubernetes Vanilla: Container Orchestrator
- Ansible and Packer: GitOps management
- Helm and Kustomize: GitOps management
- Opensearch: Logs management Solutions
- Velero: Native backup solution for Kubernetes
The entire solution was implemented through the use of GITOPS and DEVOPS methodologies and best practices.
This type of approach resulted in a solution that was so functional that the client itself decided to use it to deliver services in production environments.
For Software Release Management, we started from the tools the customer was already using and extended their functionality.
The focus of this article is infrastructure modernization.
GitOps and DevOps Methodology.
GitOps is a methodology that uses Git as the single source of truth on which to define infrastructure as code. GitOps, allows standardization of management and configuration workflows of different infrastructure components, increasing security and consistency across environments.
Using this methodology, the infrastructure is managed as code and is extended to the use of CI/CD.
Through the adoption of specific automation tools and collaboration best practices, the DevOps methodology simplifies the application lifecycle, allowing the release of new Software releases to be managed quickly, frequently and efficiently.
Implementation
The infrastructure is created, configured and maintained using the following frameworks and tools:
- Packer: Image build automation
- Ansible: IT Automation Engine
- Gitlab Pipeline: CI/CD Solution
Following GitOps best practices, The code defining the state of the different infrastructure components, has been made available in versioned mode on a dedicated Gitlab repository.
Below is a high-level logical diagram of what was accomplished:
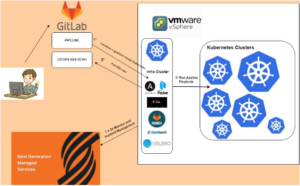
The VMs of the Kubernetes cluster, are created by VSPHERE vm-templates managed directly by Packer within dedicated Ansible roles.
The OSs of the VMs, are installed and configured via Kickstart files, defined within the Packer hcl.
In this way, it was possible to version the OS configurations as well.
The Ansible playbook, manages, the lifecycle of all components of the ecosystem:
Kubernetes Vanilla::
- Managing the deployment of VMs dedicated to the K8s cluster on vSphere.
- Installing and configuring Kubernetes Vanilla clusters.
- Installing and configuring add-ons to the kubernetes cluster:
- Container Engine
- CNI
- CSI
- Ingress Controller
- Velero Node-Agent
- Gitlab-runner
- Vault agent
- Dynatrace agent
- Release update management of Kubernetes Vanilla clusters and add-ons.
- Management of scale up and scale down operations of Kubernetes clusters.
Hashicorp Vault:
- Setup via operator
- Kubernetes auth modules configuration
- Roles Configuration
- Policy definition
- Backup Configuration
Opensearch:
- Setup cluster Opensearch
- Configuration according to defined specifications rectory
- Active Directory authentication module configuration
- Data aging policy definitions
- Configuring backups via Snapshot
- Cluster up/down scales
- Update release
Velero:
- Installation by Operator
- Defining backup policies
- Release upgrade
- Upgrade di release
The ansible playbook, built and maintained by Sorint, has been integrated with a Gitlab Pipeline built specifically to manage its execution:
This approach made it possible to:
- Track every single change to the infrastructure
- Keep cluster configurations consistent with what is defined in the Gitlab repository.
- In the event of a fault/disaster, immediate recovery of Kubernetes clusters and managed infrastructure components.
- Centralized MultiCluster Kubernetes management.
- Provisioning of new Kubernetes infrastructure quickly, easily and automatically.
- Upgrading fast and secure ecosystem component releases.
- No subscription fees.
In addition, the customer decided to purchase our NGMS (Next Generation Managed Services) service that can monitor and intervene in case of Incidents on the different ecosystem components in 24×7 mode.


